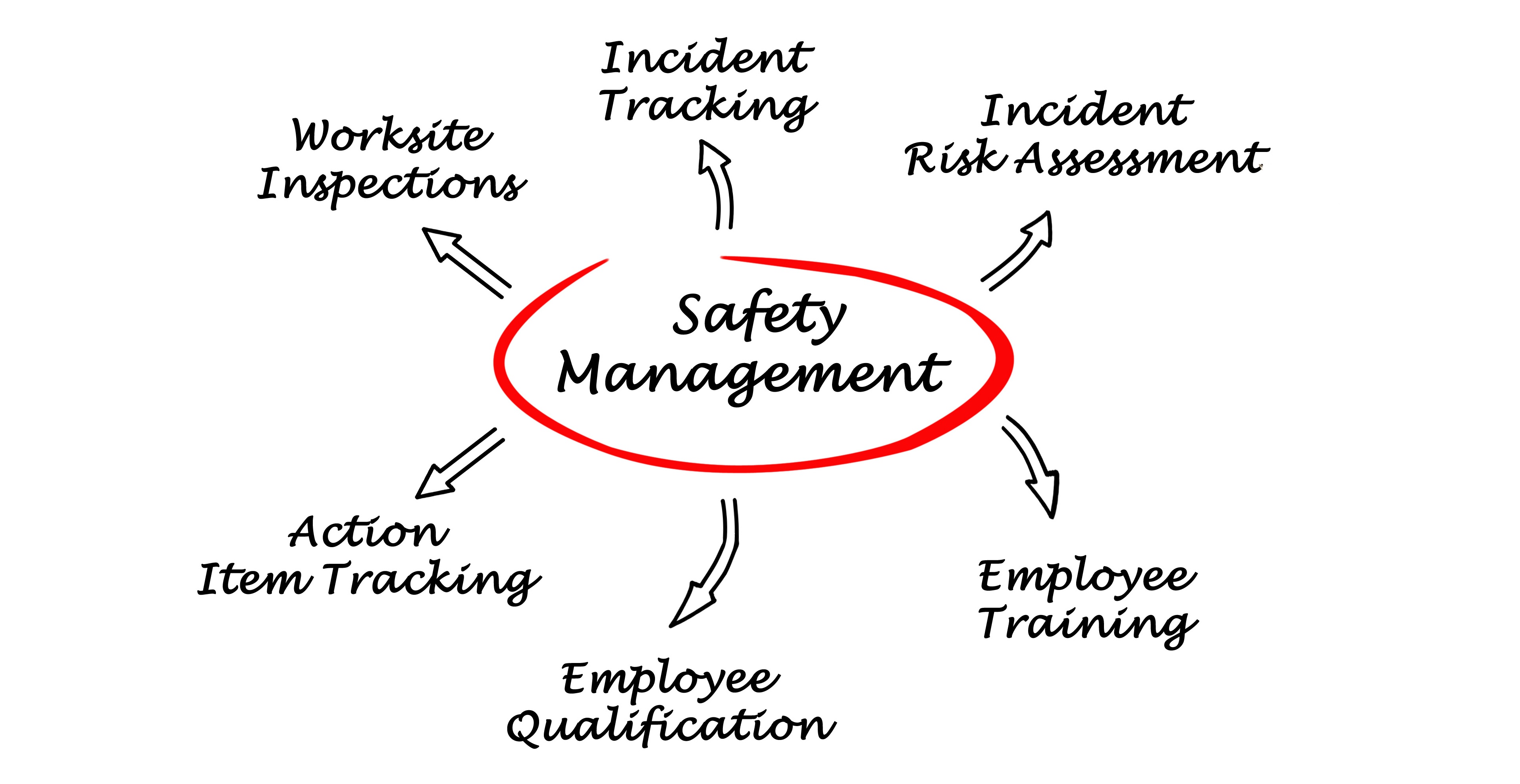
Good Day’s Work is excited to celebrate National Farm Safety Week this year, and we hope that you will do what you can to join us in our mission to promote a safer environment in agriculture. Farm injuries and fatalities are preventable through education, and this awareness week serves as a good reminder to rural communities that agriculture is one of the most dangerous occupations in the U.S.
The theme “Farm Safety…A Legacy to be Proud of ” reminds local and rural communities that agriculture is one of the most dangerous occupations in the U.S. The most recent data from the U.S. Department of Labor indicates that in 2014 farming accounted for 568 fatalities, with an estimated 70,000 injuries.